Herd immunity, or community immunity, is a great term we hear bandied about lately. Herd Immunity means lowering a population's susceptibility to a disease to the point where a disease cannot remain endemic, introduced outbreaks fade without intervention, and the vulnerable are protected by the immunity of the herd. Let's learn about how we actually achieve herd immunity with vaccination and "how much is enough?" We'll examine the basis of epidemic theory, and examine Measles vaccination and the Measles current outbreak as an example. Fascinating stuff ahead!
We can't learn everything in school. Most nursing schools offer Community/Public Health, but the epidemiology covered is largely conceptual. Few nurses see the most basic equations that underpin it. What did your school teach?
Arithmophobes, don't fear, there is very little math here. I'll keep it elegantly simple, nothing but elementary school arithmetic. It is not possible to include all details and variables in the scope of this article.
Let's talk about epidemic theory!

Some diseases are very contagious. Others are less easy to spread. How can we quantify the propensity of a disease to spread? We start simple with the Basic Reproductive Rate:
R0 = Number of secondary infections from one index case in a fully susceptible population
Some diseases are very contagious like Pertussis and Measles. Influenza has a R0 of 2- 3.
If we have an index case of measles in an unvaccinated population, the second generation will have 12-18 infections. The third generation could have 144-384 infections. This is keeping it very simple. I promised. No matrix calculus! You can see, the outbreak grows with each generation. If I want the outbreak to shrink, I need an Effective Reproductive Rate ® less than 1, where each generation produces fewer infections than it started with. There are several ways to lower R, ranging from vaccination to quarantine.
Herd Immunity
Herd immunity, or community immunity, means we have an effective reproductive number less than 1 due to immunity in the population.
Q0 = Threshold of the population that has to be immune to achieve R<1
Q0 = (1- (1/R0))
Great video illustrating Herd Immunity
We can achieve herd immunity for measles somewhere in the range Q0=0.91-0.95 and the converse 1-Q0, or 1/R0, is the maximum susceptibility rate of a population to still have herd immunity (5-9% population susceptible). But 91-95% isn't the same as the necessary vaccination rate for herd immunity. Let me break it down. Q0 is the minimum immunity rate we need in a population to make outbreaks immediately self-limiting; the minimum vaccination rate required to achieve Q0 is higher than Q0. Consider that we don't try to vaccinate everyone and vaccination does not always result in immunity.
We want to know:
V0 = Minimum vaccination rate, of those we can vaccinate, to achieve herd immunity?
The extra variables we need to know:
P = percentage of the population we could be vaccinating
C = seroconversion rate, percent of those vaccinated who become immune
Therefor:
V0 = Q0/(C*P) = (R0-1)/(R0*C*P)
For our measles example, recommended vaccinations are occurring at ages 12-15 months, so we have roughly 2% of the population who are susceptible, vaccination not due, so P = 0.98 in this example. Our seroconversion rate © is 95-97% (we can make this 99% if we redose MMR at 4-6 years) so we will just assume C = 0.97 to avoid complexity in this example. When we do the math we see:
V0 = 0.964 - 0.993
So That Is How Much?
99%? That is a really high percentage of people that need to be vaccinated on schedule. Luckily, more complex models show we don't quite need 99%, but it is still high, higher than Q0. It should now be obvious why exemptions are a huge problem. Medical exemptions are incredibly few, almost negligible in rate for infants and toddlers. But personal and religious exemptions create a problem. 4% exemptions and we have no hope of herd immunity. Colorado has an exemption rate over 18% right now for MMR. The more exemptions, the faster and wider an outbreak spreads. Worse yet, studies show vaccine refusers cluster... so in a community there is a very high R, creating a larger than expected infected population that then exposes the rest of the population. Remember, ~1-3% of the vaccinated are still susceptible to measles due to no serconversion or becoming immunocompromised.
Vaccine refusers who are misinformed or who don't understand the impacts on society are a major problem, but there is another flavor. Some people ascribe to the disproven theory that infants and toddlers cannot handle CDC recommended immunizations and they should be delayed. Dr. Bob Sears popularized this idea and invented an alternate schedule to go along with it. He recommends age 5 for vaccinations like MMR. What if everyone followed that? 7% of the population is under age 5. Calculate V0 for P=0.93 and we get impossible values. If everyone followed Dr. Sears vaccinate-at-entry-to-school philosophy, we would have a national immunity rate to Measles
Herd immunity could protect the vulnerable
With a highly contagious disease like measles, even in the best of circumstances, even with the highly effective vaccine, we operate in the grey zone maintaining of herd immunity which is why we still have to have some public health measures to combat new outbreaks. We are not in the best of circumstances thanks largely to anti-vaxxers. The US has a vaccination rate worse than Mexico. The US rate grazes the bottom end of the herd immunity range. We have to make up ground with public health intervention to stem outbreaks. CDC, Public Health Departments, and healthcare providers are educating the public, examining records, tracing contacts, isolating measles cases, and quarantining exposed susceptible people.
Over the edge of herd immunity - Needs a helping hand
Without these public health measures, measles would become endemic in the US again. It still could end up that way. Luckily, the Supreme Court ruled that the government has the right to mandate vaccines and enforce public health measures including quarantine.
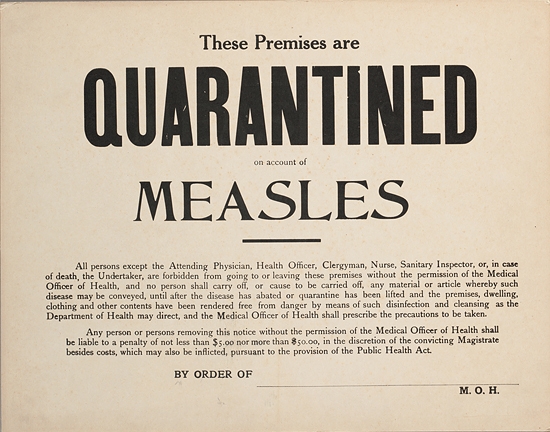
Vaccination sometimes spawns talk about freedom and rights. The math above makes it clear that individual decisions to vaccinate affect all of society. Public health measures range from low key to draconian. Lower vaccination rates require more intrusive and draconian public health measures to stem the tide of an outbreak. How do you feel about this?
This Measles outbreak has spread to 18 states and Mexico with hundreds of people are quarantined or isolated. The outbreak would not be so big if more people vaccinated. The outbreak would be worse without the public health establishment fighting the outbreak. It is not over yet. It will happen again.
Nurses have many roles in this battle for public health, depending on our specialty. All of us can educate and advocate. What is your role?
References:
Herd immunity: history, theory, practice. - PubMed - NCBI (Free text version)
Notes on R0
CDC - Pinkbook: Measles Chapter - Epidemiology of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
The association between intentional delay of vaccine administration and timely childhood vaccination coverage.
Addressing Parents' Concerns: Do Multiple Vaccines Overwhelm or Weaken the Infant's Immune System?
The problem with Dr Bob's alternative vaccine schedule.
Global Health Observatory Data Repository
Colorado kindergartners have lowest measles vaccination rate in the nation
Chicago-Area Day Care Says 5 Infants Diagnosed With Measles
Jacobson v. Massachusetts
Morgan's Louisiana Company v. Board of Health of the State of Louisiana/Opinion of the Court



LadyFree28, BSN, LPN, RN
8,429 Posts
BUMP.