- Community
-
Programs
- Schools
-
Careers
- RN Specialties
- Best RN Jobs and Salaries
- Aesthetic Nurse
- Nursing Informatics
- Nurse Case Manager
- NICU Nurse
- Forensic Nurse
- Labor and Delivery Nurse
- Psychiatric Nurse
- Pediatric Nurse
- Travel Nurse
- Telemetry Nurse
- Dermatology Nurse
- Nurse Practitioner
- Best NP Jobs and Salaries
- Family NP (FNP)
- Pediatric NP
- Neonatal NP
- Oncology NP
- Acute Care NP
- Aesthetic NP
- Women's Health NP
- Adult-Gerontology NP
- Orthopedic NP
- Emergency NP
- Psychiatric-Mental Health NP (PMHNP)
- APRN
- Nurse Educator
- Nurse Administrator
- Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS)
- Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)
- Resources
- Education

CaringGerinurse525
117 Posts
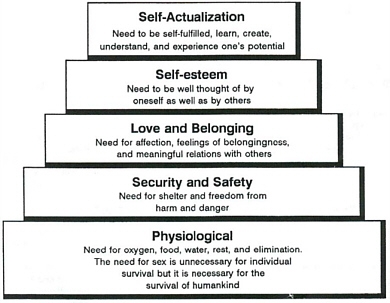
I have a project due Tuesday where I have to rank my NANDAS in the priority of care as well as according to Maslows Levels. I am confused about the physical ones...here is what I have so far...
Does this look right?
Nanda, Priority of Care, Maslows level Self-care deficit
#1 PhysiologicalRisk for Falls.
#4 safety and security Risk for impaired skin integrity.
#2 physiological Risk for infection.
#5 safety and security Risk for activity intolerance.
#3 physiological Risk for compromised resilience.
#6 safety and securityRisk for impaired social inter.
#7 love and belonging Risk for powerlessness.
# 8 self-esteem